The key to market direction as I have said many times is ORDERFLOW. "Orderflow" has become a much over used word in the many years since I started this blog in 2009.
The issue is that most wanna be traders have no idea of what orderflow is. I guess I have a big advantage of being a an ex local pit trader as that was at the sharpest edge of orderflow.
Any picture, setup or trading idea can be completely invalidated if the orderflow changes: if enough orders come into the other direction to your trade. Before the latest technology of which NinjaTrader 8 is a great example, we nhad to look at the footsteps of orderflow: indicators. This was not perfect. Indicators have now become part of the context.
Today's chart shows how easy it is to see orderflow. However, the orderflow needs to be seen in context to understand the probabilities of what will happen next. Pete Steidlmayer's teachings have even more relevance now that we can see orderflow clearly.
Thursday, July 28, 2016
Friday, July 22, 2016
Interfacing Old Mobile Phone (Siemens,Nokia,Sony Ericsson) With Pic Or Arduino. (Cheapest GSM Project)
Interfacing Old Mobile Phone With Pic Or Arduino. (Cheapest GSM Project).
Hi my dears followers, Like it is mentionned in the article title. Today i m trying to demonstrate how we could make a GSM project using any type of MCU Connected to an Old mobile phone.
The idea was not the same used usually, In Fact i m not going to use a GSM Module like SIM900.
To make this real idea I collect a lot of old mobile phone

Hi my dears followers, Like it is mentionned in the article title. Today i m trying to demonstrate how we could make a GSM project using any type of MCU Connected to an Old mobile phone.
 |
| MCU Interfacing |
The idea was not the same used usually, In Fact i m not going to use a GSM Module like SIM900.
 |
| GSM usually used module |
The idea is since there is many old mobile phone (cheap phone) why not to hack their GSM Circuit to used an our project.
You dont have to collect many mobile phone like i did. To make your project. Just look for one, google it and collect any information could help you.
Information like:
Information like:
- Which Communication Protocol is using
- Current and Voltage Adaptation
- Is there a naked TX/RX like in Nokia 1100
Nokia 1100 - F-Bus, M-Bus, Both, None ???
- Sms Text,PDU ??
This project idea was given to me by a friend of mine, he explain me that was very nice to have an GSM based Control project without using a module but by using a simple old phone like this one (Nokia 1100).
I remember that I saw this guy trying to connect Tx Rx pins of Nokia 1100 to Tx Rx pins of a simple PIC (16F877). In this moment I noticed thats there is a mistake because the voltage in both side is different.
I thought thats the only problem is here, and I start thinking why to pay 50 � for a GSM module when we could use a simple old mobile phone.
I remember that I saw this guy trying to connect Tx Rx pins of Nokia 1100 to Tx Rx pins of a simple PIC (16F877). In this moment I noticed thats there is a mistake because the voltage in both side is different.
I thought thats the only problem is here, and I start thinking why to pay 50 � for a GSM module when we could use a simple old mobile phone.
In fact mobile phones are different from one to other.
Most of Nokia Mobile phone and here i m talking about Nokia 3310, Nokia 1100,... used F-Bus and M-Bus protocol in their GSM network circuit.
Most Nokia phones have F-Bus and M-Bus connections that can be used to connect a phone to a PC or in our case a microcontroller. The connection can be used for controlling just about all functions of the phone, as well as uploading new firmware etc. This bus will allow us to send and receive SMS messages.
M-Bus is a one pin bi-directional bus for both transmitting and receiving data from the phone. It is slow (9600bps) and only half-duplex. Only two pins on the phone are used. One ground and one data. M-Bus runs at 9600bps, 8 data bits, odd parity, one stop bit. The data terminal ready (DTR) pin must be cleared with the request to send (RTS). This powers the electronics in the cable and I think it sets it for M-Bus operation.
F-Bus is the later high-speed full-duplex bus. It uses one pin for transmitting data and one pin for receiving data plus the ground pin. Very much like a standard serial port. It is fast 115,200bps, 8 data bits, no parity, one stop bit. For F-Bus the data terminal ready (DTR) pin must be set and the request to send (RTS) pin cleared.
F-Bus is not the same protocol usually used in GSM module so to use it you have to make your own F-bus Cable converter.
- Nokia Family
Most of Nokia Mobile phone and here i m talking about Nokia 3310, Nokia 1100,... used F-Bus and M-Bus protocol in their GSM network circuit.Most Nokia phones have F-Bus and M-Bus connections that can be used to connect a phone to a PC or in our case a microcontroller. The connection can be used for controlling just about all functions of the phone, as well as uploading new firmware etc. This bus will allow us to send and receive SMS messages.
M-Bus is a one pin bi-directional bus for both transmitting and receiving data from the phone. It is slow (9600bps) and only half-duplex. Only two pins on the phone are used. One ground and one data. M-Bus runs at 9600bps, 8 data bits, odd parity, one stop bit. The data terminal ready (DTR) pin must be cleared with the request to send (RTS). This powers the electronics in the cable and I think it sets it for M-Bus operation.
F-Bus is the later high-speed full-duplex bus. It uses one pin for transmitting data and one pin for receiving data plus the ground pin. Very much like a standard serial port. It is fast 115,200bps, 8 data bits, no parity, one stop bit. For F-Bus the data terminal ready (DTR) pin must be set and the request to send (RTS) pin cleared.
F-Bus is not the same protocol usually used in GSM module so to use it you have to make your own F-bus Cable converter.
Personally I found a bit of Difficulty using this one specially when i found in the net that there is other phone like Siemens or Sony Ericsson could simply support AT command.
All what you have to do is to use their charging cable.
- > Vbatt - Power Charging (used for charging).
- > Gnd - GND (main ground).
- > Tx connected to MCU RX (using a resistor to limit current ).
- > Rx connected to MCU TX (using a voltage devider from 5v to ~2,75v).
- > CTS need to be connected to ground in order to work
- > RTS
- > DCD
- > Audio P - AUDIO L
- > AUDIO - GND
- > Audio N - AUDIO R
- > GND Mic
- > EPP EPP 1 (EXT MIC.)
Noting is easier than this :)
So to connect this mobile phone to an Arduino or a PIC all what you have to do is to follow this. The resistors using is to adept current and voltage between the phone and the MCU.
So to connect this mobile phone to an Arduino or a PIC all what you have to do is to follow this. The resistors using is to adept current and voltage between the phone and the MCU.
 |
| Arduino interfacing |
 |
| Pic Interfacing |
Now let's speak about program after connecting the phone to the MCU.
- We send serially AT, We received OK . Fine thats Work :D
- To check SMS format we send AT+CMGF=0 , We received OK . Fine this phone support PDU Format message.
- We send AT+CMGF=1 and we received error :/ here is the problem . the phone cant support text message format.
There is no problem if we convert our text message to PDU format before send it or convert received text from PDU format to TEXT.
Here i give you two link, the first is to convert PDU to Text and the second is the inverse.
First One
Second One
Here i give you two link, the first is to convert PDU to Text and the second is the inverse.
First One
Second One
Lets Code...
void createSMS(){ phone.println("AT+CMGS=66"); delay(2000); phone.print("07911256536621F801000B911296683049F300043554686973206973206D652069206D2061796D656E206C6163686B68656D2C2057656C636F6D6520696E206D7920626C6F6773697465"); phone.write(0x1A); // Ctrl+Z phone.write(0x0D); //CR phone.write(0x0A); //LF}...and it works ! ...an SMS with "This is me i m aymen lachkhem, Welcome in my blogsite" on it was send by calling the createSMS() function.
Wednesday, July 13, 2016
Robotic Arm Based on ATMEGA MCU, Controlled By Windows C# Application
Hello , Today I m changing my publishing language from French to English for many reasons, one of them the countries where the followers come from and the first language that is used over there.
For those who want their french versions they have just to ask me Contact Me.
So let's Begin.
For those who want their french versions they have just to ask me Contact Me.
So let's Begin.
 |
| The Complet Project |
Like it is mentionned in the title of this post, I m going to make a Soft/Hard parts to have finally our Robotic Arm working.
This robotic arm is controlled with :
- Soft : Windows Form Application made with C# in Visual Studio 2012.
- Atmega 328 like a principale MCU.
The Soft Part was done in Visual Studio 2012, In fact it is a little bit complicated for a beginner programmer because it include many parts.
- More than one only frame
- Password/Login Interface
- User/Super User interface
- Data Base
Password/Login InterfaceThis one will give the possibility to only registred users to control the robotic arm.
User/Super user interfaceThe super user is like a master because he have the right to modify or delete or even add a normal user.
Data Basewe want to print and save the position of the robotic arm every 60 secondes in an array composed from 4 collumns (User,Time,Date and Position).
Now the Hard side of this project is how MCU like ATmega 328 is able to control many servo motors in the same time.
We have to know exactly how a MCU could control one servomotor and for this:
I recommend to read this post click me.
 |
| How servos work |
The answer is UART (universal Asynchrone Receiver Transmitter) and for those how dont know it yet, just take a look here Click Me.
Our goal is not to control only one but 4,5,6 or even more in the same moment. and that's need a few things to understand like how to manage the energy and how program will be like.
Let's imagine thats we have a tram including some data who will be sent from the soft side of the project and readable in the MCU.
Here the MCU will react with every data one by one, converting every one to an information or order to the servo-motors.
Why we chose Atmega 328 ?
| Serial Communication |
Why we chose Atmega 328 ?
- ATmega 328 is cheaper than Arduino
- Programming ATmega is easier than PIC or 8051 or one other MCU.
We are all agree that's programming Arduino is the easier one so let's take advantage from Arduino here.
If you read this:Arduino .
Arduino Uno for exemple is a platform who contains like a principal MCU ATmega 328. so you have just to follow those steps:
- Take out this ATmega 328
 |
| ATmega 328 |
- Replaced by the one that's we are going to used in your project
- Type your program like you are programming Arduino
- Take it back
You have just to remember every I/O in Arduino uno is connected to wich one in ATmega328.
For that Take a look here
 |
| Arduino/ATmega328 Connection Pin |
After Programming our MCU, we have to add some electronics composants to make it work like (Capacitor,Quartz, TTL/Serial Converter,....).
Serial/TTL Converter is the circuit able to make data passed from MCU readable in the computer. The same comportement in the other direction.
This is The complet Circuit that's you have to do:
Serial/TTL Converter is the circuit able to make data passed from MCU readable in the computer. The same comportement in the other direction.
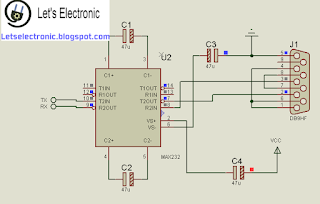 |
| TTL/Serial Converter |
This is The complet Circuit that's you have to do:
 |
| ROBOTIC ARM BY AYMEN LACHKHEM |
And The Program that we will place it ine the MCU's Mmemory is:
/* Robotic Arm Controlled by C# Windows Application
* Contact Me : Aymenlachkem@gmail.com */
#include <Servo.h>
Servo Servo1, Servo2, Servo3;
String readString, firstString, secondString, thirdString;
int Goal1, Goal2, Goal3;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Servo1.attach(9);
Servo2.attach(10);
Servo3.attach(11);
}
void loop() {
boolean Done = false ;
while (Serial.available()) {
delay(1);
if (Serial.available() >0) {
char c = Serial.read();
readString += c;
} }
if (readString.length() == 1){ONE_BUTTON_CONTROL();}
if (Serial.read() == '9'){if (Done){Serial.write("Done"); }}
if (readString.length() == 9) {Command_Control();}
}
void ONE_BUTTON_CONTROL(){
if (Serial.read() == '7'){
Servo1.write(90);
Servo2.write(90);
Servo3.write(90);
delay(1000);}
if (Serial.read() == '8'){
Servo1.write(0);
Servo2.write(0);
Servo3.write(0);
delay(1000);}
if (Serial.read() == '1')
{
Servo1.write(Servo1.read()+1);
}
if (Serial.read() == '2')
{
Servo1.write(Servo1.read()-1);
}
if (Serial.read() == '3')
{
Servo1.write(Servo2.read()+1);
}
if (Serial.read() == '4')
{
Servo1.write(Servo2.read()-1);
}
if (Serial.read() == '5')
{
Servo1.write(Servo3.read()+1);
}
if (Serial.read() == '6')
{
Servo1.write(Servo3.read()-1);
}
}
void Command_Control(){
{
firstString = readString.substring(0, 3);
secondString = readString.substring(3, 6);
thirdString = readString.substring(6, 9);
char carray1[5];
firstString.toCharArray(carray1, sizeof(carray1));
Goal1 = atoi(carray1);
char carray2[5];
secondString.toCharArray(carray2, sizeof(carray2));
Goal2 = atoi(carray2);
char carray3[5];
thirdString.toCharArray(carray3, sizeof(carray3));
Goal3= atoi(carray3);
boolean Done = ((Servo1.read() == Goal1) && (Servo2.read() == Goal2) && (Servo3.read() == Goal3));
while (!Done) {
int position1 = Servo1.read();
int position2 = Servo2.read();
int position3 = Servo3.read();
if (position1 < Goal1){
Servo1.write(position1 + 1);
}
if (position1 > Goal1){
Servo1.write(position1 - 1);
}
if (position2 < Goal2){
Servo2.write(position2 + 1);
}
if (position2 > Goal2){
Servo2.write(position2 - 1);
}
if (position3 < Goal3){
Servo3.write(position3 + 1);
}
if (position3 > Goal3){
Servo3.write(position3 - 1);
}
delay(20);
}}}
Let's Talk about Soft part of This project :
A windows Application written with C# inside VisualStudio 2012 who have acces to every port Com in the computer will detect our Circuit Com and control the robotic arm through him
To Make a C# project like i mentionned before there is two part of work to do (Design/Program).
I m working an a new playlist youtube video tutoriel about C# electronic oriented. As soon as possible i will publish it here.
I m working an a new playlist youtube video tutoriel about C# electronic oriented. As soon as possible i will publish it here.
And here is the robotic Arm Application frame by frame:
 |
| Frame 1 |
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem
{
public partial class Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem : Form
{
public Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem()
{
InitializeComponent();
textBox5.PasswordChar = '*';
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void dateTimePicker1_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ProcessStartInfo startInfo = new ProcessStartInfo("iexplore.exe", "http://https://letselectronic.blogspot.com/p/blog-page.html/");
Process.Start(startInfo);
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("In Construction");
}
private void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("In Construction");
}
private void button2_Click_1(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var myLines = new List<string>();
myLines.Add("Hello, This Windows application give their Users the ability to control serially or with wirless communication a 3 axes robotic arm.");
myLines.Add("- The MCU used is The high-performance Atmel 8-bit AVR RISC-based microcontroller ATmega 328 ");
myLines.Add("- The Control Application was made in Visual Studio 2012, written using C# ");
myLines.Add(" ");
myLines.Add("----------------------------------------- Blog: Letselectronic.blogspot.com -------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
myLines.Add("----------------------------------------- Contact: Aymenlachkem@gmail.com --------------------------------------------------------------------------");
myLines.Add("----------------------------------------- Youtube Channel: Youtube.com/c/AymenLachkem ---------------------------------------------------");
textBox1.Lines = myLines.ToArray();
}
private void Visit_My_Blog_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ProcessStartInfo startInfo = new ProcessStartInfo("iexplore.exe", "http://www.letselectronic.blogspot.com/");
Process.Start(startInfo);
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Add_user frm = new Add_user();
frm.Show();
}
private void Get_The_Code_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Just Contact Me :)");
}
private void Login_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string super_user = "aymen_lachkhem";
string super_pass = "engineer";
if ((textBox4.Text == super_user || textBox4.Text == Add_user.user) && (textBox5.Text == super_pass || textBox5.Text == Add_user.pass))
{
Main frm = new Main();
frm.Show();
MessageBox.Show("Welcome");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Check Again Please");
}
}
}
}
 |
| Frame 2 |
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem
{
public partial class Add_user : Form
{
public static string user = "0000";
public static string pass = "0000";
public Add_user()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Hide();
}
private void Exit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void Register_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox4.Text == "" || textBox5.Text == "" || textBox6.Text == "")
{
MessageBox.Show("Please provide User Name and Password");
return;
}
else
{
if (textBox5.Text == textBox6.Text)
{
user = textBox4.Text;
Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem frm = new Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem();
pass = textBox5.Text;
Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem frm1 = new Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem();
MessageBox.Show("Welcome");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Differents Passwords");
}
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO.Ports;
namespace Robotic_Arm_By_Aymen_Lachkhem
{
public partial class Main : Form
{
public Main()
{
InitializeComponent();
getAvailablePorts();
}
void getAvailablePorts()
{
string[] Ports = SerialPort.GetPortNames();
portcom.Items.AddRange(Ports);
}
private void label1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void connecter_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (portcom.Text == "" || baudrate.Text == "")
{
textbox1.Text = "Please select port setting ? ";
}
else
{
serialPort1.PortName = portcom.Text;
serialPort1.BaudRate = Convert.ToInt32(baudrate.Text);
progressBar1.Value = 100;
}
}
catch (UnauthorizedAccessException)
{
baudrate.Text = "Unauthorized Access";
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Close();
progressBar1.Value = 0;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void annuler_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Hide();
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("6");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("5");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("3");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void turn_on_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("7");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void turn_off_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("8");
serialPort1.Close(); serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button10_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox3.Clear();
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("9");
string retour = serialPort1.ReadLine();
textBox3.Text += retour + "\n";
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button8_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("1");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button7_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("2");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write("4");
serialPort1.Close();
}
private void button9_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
serialPort1.Open();
serialPort1.Write(textBox2.Text);
serialPort1.Close();
textBox2.Clear();
}
}
}
Built your application, Get your file.exe and the Setup. Like always this is a video for more details.
I have all files of this project collected in compressed directory so just contact me to have your free files.
See you Soon AYMEN LACHKHEM
Sunday, July 3, 2016
Interfacing GSM with PIC 18F4550
Bonjour, Aujourd'hui je viens avec un autre exemple de la manipulation du PIC18F4550, Comme il est inclut au titre de cet article aujourd'hui je vais vous expliquer comment interfacer un microcontr�leur comme le PIC18F4550 avec un tel module GSM.
Il faut savoir avant tout:
- C'est quoi le module GSM
- C'est quoi les commandes AT
- C'est quoi l'UART
- Comment envoyer un SMS
- Comment r�aliser un appel vocal.
La num�rique facile d�finisse GSM comme �tant une norme de t�l�phonie mobile. On parle de r�seau GSM pour d�signer le r�seau num�rique de t�l�phonie mobile. Bien qu'on l'appelle aussi r�seau de 2 �me g�n�ration, c'est en r�alit� le premier r�seau d�velopp� avec ampleur dans le monde. On parle aussi de GSM lorsqu'on d�signe les t�l�phones mobiles utilisant ce r�seau pour communiquer.
Le "DCS 1800" utilise les fr�quences comprises entre 1710-1880 MHz.
- le GSM 850, utilisant les fr�quences situ�es entre 824 et 894 MHz.
- le GSM 1900 (appel� PCS 1900), utilisant les fr�quences entre 1850 et 1990 MHz.
Le "DCS 1800" utilise les fr�quences comprises entre 1710-1880 MHz.
- le GSM 850, utilisant les fr�quences situ�es entre 824 et 894 MHz.
- le GSM 1900 (appel� PCS 1900), utilisant les fr�quences entre 1850 et 1990 MHz.
GSM veut dire Global System for Mobile Communications. Il pr�sente un fonctionnement cellulaire : au coeur de chaque cellule, qui d�signe une zone g�ographique plus ou moins �tendue, il y a une antenne relais qui permet de faire le lien entre les t�l�phones mobiles et le r�seau. Le r�seau permet de passer d'une cellule � une autre sans interrompre la communication et sans que l'utilisateur ne s'en rende compte.
Le r�seau GSM utilise les fr�quences situ�es dans la bande 890-960 MHz.On parle du "GSM 900" dans ce cas.
D'autres r�seaux, connus sous un nom diff�rent, sont aussi des r�seaux GSM, mais utilisant d'autres bandes de fr�quences.
Les commandes AT sont d�finies dans la norme GSM 07.07(pour les SMS cf. GSM 07.05). AT est l�abr�viation de ATtention. Ces 2 caract�res sont toujours pr�sents pour commencer une ligne de commande sous forme de texte (codes ASCII). Les commandes permettent la gestion compl�te du mobile.
- TE : Terminal Equipment (envoi et affiche les commandes.
- TA : Terminal Adaptator (interface entre l�utilisateur et le mobile).
- ME : Mobile Equipment.
Un UART,Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter, est un �metteur-r�cepteur asynchrone universel.
En langage courant, c'est le composant utilis� pour faire la liaison entre l'ordinateur et le port s�rie . L'ordinateur envoie les donn�es en parall�le (autant de fils que de bits de donn�es). Il faut donc transformer ces donn�es pour les faire passer � travers une liaison s�rie qui utilise un seul fil pour faire passer tous les bits de donn�es.
Un DUART (Dual Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) combine deux UART dans une seule puce. Un USART (Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) peut communiquer de fa�on synchrone.
Aujourd'hui, les UART sont g�n�ralement int�gr�s dans des composants comme des microcontr�leurs. Ils ne sont dans ce cas plus un composant � proprement parler, mais une fonction p�riph�rique du composant.
Le module UART est repr�sente au PIC18F4550 sur les deux pins TX et RX.
Alors pour conclure le travail qu'on va faire ici on pourra dire qu'on aura une discussion instantan�e entre deux composantes �lectroniques, le premier c'est le microcontr�leur et le deuxi�me c'est le module GSM.
- Le Module GSM il va lire les commandes AT et les transmettre on des actions bien d�finis.
- Le Pic 18F4550 Va a travers sont UART transmettre les commandes AT.
Alors commen�ons un test virtuel sur la Proteus ISIS en rempla�ant le Module GSM par un Virtuel Terminal ou une interface qui sera seriallement virtuellement � travers VSPD reli�. On ajoute un Pic18F4550, quelques boutons poussoirs et quelques condensateurs.
La programmation est toute � fait simple, on va que discuter avec l'UART du PIC18F4550 d'une fa�on artificielle et au but d'envoyer un SMS ou de r�aliser un appel vocale.
Le module GSM qui discutera avec notre �C c'est GSM shield i900.// Letselectronic.blogspot.com
// PIC184550 with 8Mhz like input Quartz
// Interfacing with GSM shield i900
void sendsms(){
UART1_Write_Text("This is AT Command should we use to send the sms");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "ATE0\r\n : This one is to make echo OFF ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "AT\r\n");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "AT+CMGF = 1\r\n " );
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "AT+CNMI=1,2,0,0,0\r\n");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "AT+CMGS=\"+xxxxxxxxx\"\r\n : You Have to replace the X's by the number ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "this is the sms: letselectronic.blogspot.com \r\n : The message that you want to send ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "Thats it :) ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
}
void voicecall(){
UART1_Write_Text("Ring .... Ring.... lool,");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "I m killing because this is the AT Command should you use ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "AT+CHFA = 1\r\n : This one is to select audio chanel");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "ATDxxxxxxxxxx\r\n : You have to replace the x's by the number" );
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "ATH\r\n : Here you Terminate your phone call");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
UART1_Write_Text( "That's it :)");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(3000);
}
void main() {
ADCON1 = 0x0F; // Configure all ports with analog function as digital
CMCON = 7; // Disable comparators
TRISB=0; // PortB like output
TRISA=1; // Port A is an input
UART1_Init(9615); // Initialize UART module at 9600 bps
Delay_ms(100); // Wait for UART module to stabilize
UART1_Write_Text("How GSM Sim 9000 Works With Pic 18F4550");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
delay_ms(2000);
UART1_Write_Text("----------------- Letselectronic.blogspot.com -----------------");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
delay_ms(2000);
UART1_Write_Text("Make your choice SMS/Voice Call by Cliking the Button");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
delay_ms(2000);
while (1) { // Endless loop
if (portA.f2 == 1) {
PortB.f0 = 1;
UART1_Write_Text("SMS Loading ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(1000);
sendsms();
UART1_Write_Text("SMS Sended ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(1000);
}
else
{
PortB.f0 = 0;
}
if (portA.f1 == 1){
PortB.f1 = 1;
UART1_Write_Text("Voice Call Loading ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(1000);
VoiceCall() ;
UART1_Write_Text("Voice Call Done ");
UART1_Write(10);
UART1_Write(13);
Delay_ms(1000);
}
else
{
PortB.f1 = 0;
}}} Mes derniers remarques sont:
- Il faut bien prendre en compte le r�glage du Quartz a utiliser avec le PIC18F4550, J'ai introduit �a dans mon article pr�c�dant.
- Il faut savoir bien les commandes utiliser avec le Module GSM pour la tache qu'on cherche (Les commandes sont tous trouvables ici).
- Initialer votre module GSM avec de r�aliser la communication (Reset button included).
- Au dessous c'est une vid�o d�monstrative de communication de PIC18F4550 avec Hyper Terminal. Suivez les d�tails et mettez moi en contact si il y a des probl�mes.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)









